
The global housing crisis generates a wide range of challenges, from those who are in situations of homelessness, to the realities of millions who face unaffordable housing conditions, overcrowding, and excessively high rents. Tackling this involves political will, the union of the state and private companies, and innovative solutions that prioritize accessibility, sustainability, and government mechanisms that enable a functioning system. Amongst all of these factors though, one thing is certain: we need to build massively in the future to improve the housing situation. The implementation of efficient construction methods, such as prefabrication and modular construction, can speed up the creation of affordable housing units, reducing construction costs and timeframes. Adopting green building practices, such as using recycled materials and designing energy-efficient structures, not only contributes to sustainability but minimizes long-term operating expenses for residents.
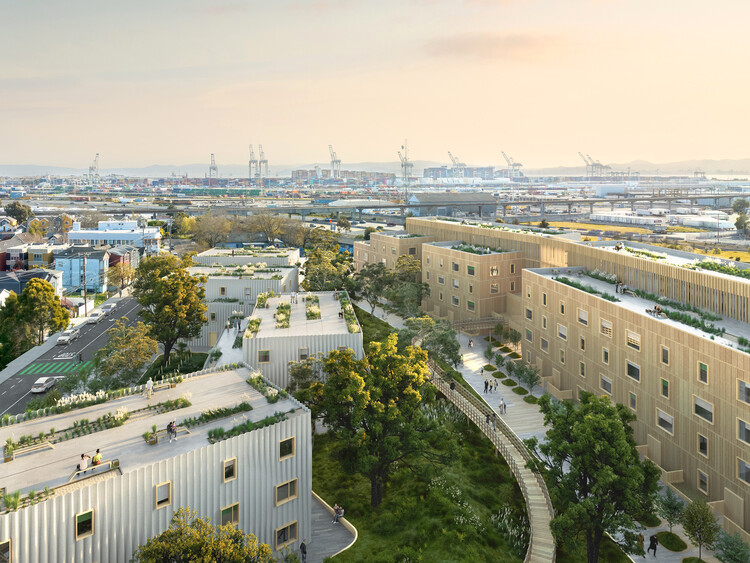
It is important to have examples of successful initiatives and solutions to raise the bar on the quality and innovations of housing projects. One such example, led by a collaborative effort, is The Phoenix project, which represents a beacon of hope for the future of sustainable, affordable, and fast construction. It will consist of 316 affordable and sustainable homes, built with about half the cost, time, and carbon footprint of a typical multi-family building in the San Francisco Bay Area. It is located in the heart of West Oakland, California, where an empty 5-acre concrete slab has been abandoned for nearly three decades adjacent to a freeway.
If at first glance the project appears to be a traditional development with sustainable characteristics –with mid-rise volumes around a central tree-lined courtyard–, it is when we delve into the design process that we understand why it is revolutionary. The work was collaborative at every stage, from conception to execution, involving MBH Architects, Factory_OS, Kreysler & Associates, Brightworks Sustainability and Ecovative, as well as the help of Autodesk and its range of design tools. We spoke to David Benjamin, Director of AEC Industry Futures at Autodesk, and Thomas VanHaren, Chief Operating Officer at Ecovative, for some valuable insights into this pioneering initiative.

Shaping the Future Through Mindful Design
David Benjamin, whose work focuses on exploring innovations for possible futures and developing partnerships and prototypes, begins by explaining that the project presents an innovative approach harnessing artificial intelligence and Forma to simplify the many complexities of design. Some of these simplifications included reducing the initial design package creation time from two weeks to six hours, and promoting faster housing delivery while allowing for greater creativity and amenity-focused designs for residents and the community.
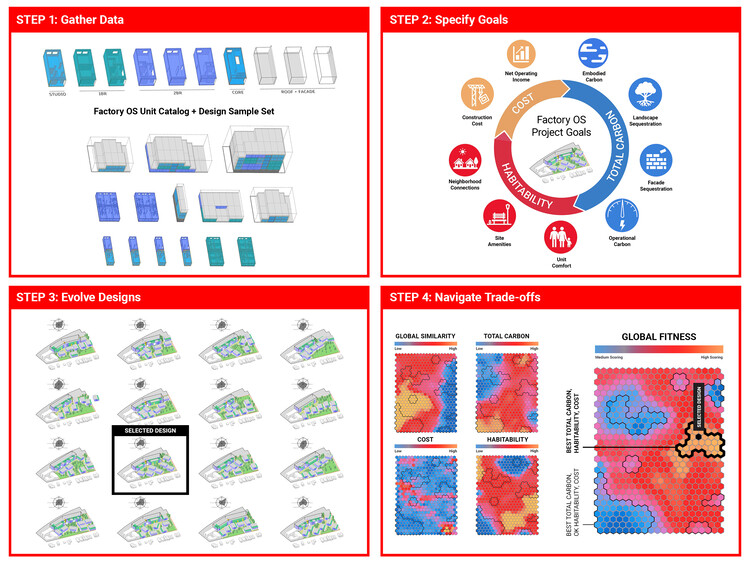
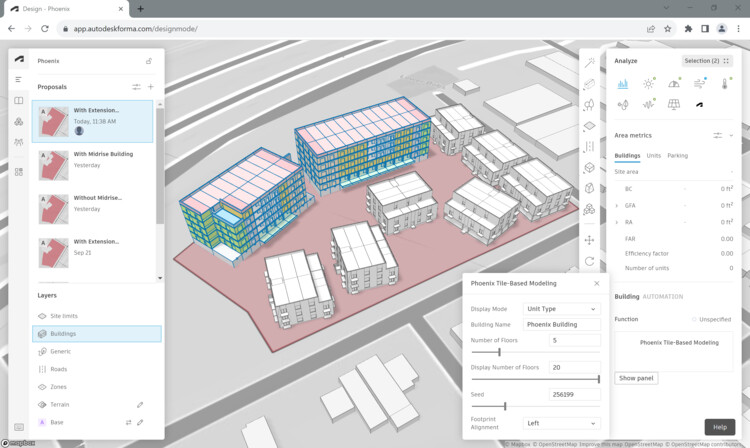
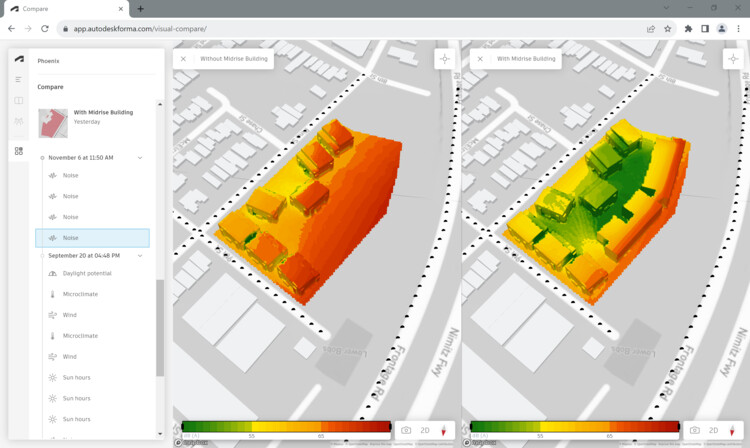
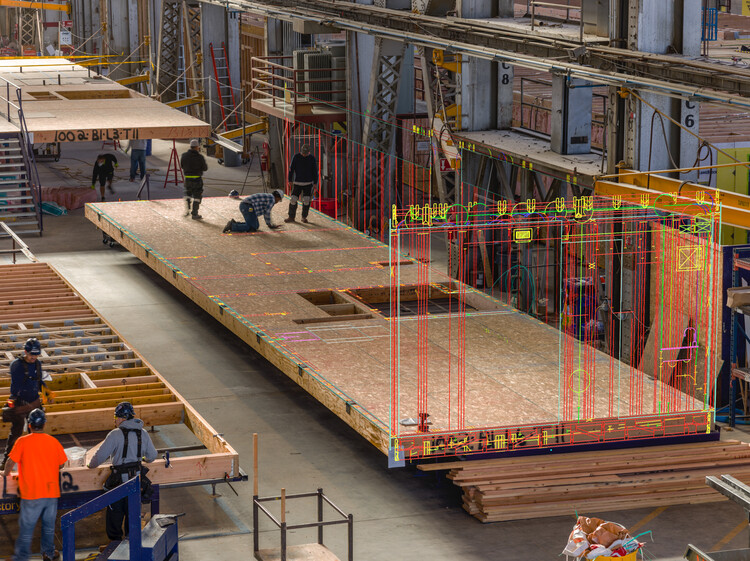
Software such as Revit and Construction Cloud facilitated the continuous flow of data from conceptual design to construction, using reusable design intelligence for prefabricated housing units, thus avoiding delays and ensuring efficient progress tracking both in the factory and on-site. Autodesk's Design and Make platform also serves as a digital thread that connects project teams and data during the design and construction phases, forming an essential component of The Phoenix's success.
The Phoenix is a demonstration that is ready to be generalized for future projects. The software workflow and its benefits can be applied to other affordable housing projects, and also to other building types like factories, labs, and offices. The new façade system is a “drop-in technology” that works with today’s building codes and construction practices. It can be used for other projects in California and many parts of the world. Now is the time to scale up. —David Benjamin
Mycelium on the Façade
A significant challenge when looking for a sustainable project lies in its envelope, which is often responsible for more than 20% of the embodied carbon. This is because finding materials with a low carbon footprint is complex due to stringent performance requirements, such as durability and fire resistance. Benjamin points out that “In terms of carbon footprint, Autodesk Forma and Autodesk Insight gave the team a platform to track and reduce the embodied carbon of the project through a first-of-its-kind façade system that combined a durable fiber-reinforced-polymer shell with a bio-material core. The resulting 38-foot-long panels are carbon-negative and they can be installed about five times faster than a standard façade system.”
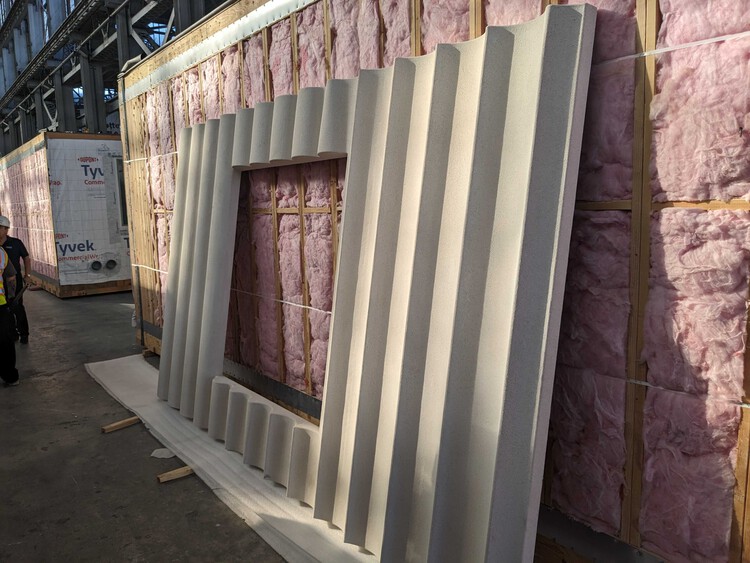


This innovation in the choice of materials is an iconic part of the project. MycoComposite mycelium-based materials have the potential to revolutionize the construction industry on several fronts. Developed by Ecovative, they offer long-lasting sustainability by integrating indefinitely into structures, and are compostable after demolition, enriching soil nutrients and ensuring a sustainable life cycle. The mixture of mycelium and plant fibers creates a lightweight, durable, flame-resistant, and insulating material, significantly reducing energy consumption, resources, and carbon emissions in production compared to conventional building materials. By bypassing energy-intensive processes and reducing waste production, MycoComposite speeds up modular construction, potentially halving the time required from two years to one. Growing components on-site using local agricultural inputs further minimizes environmental impact and construction duration. Mycelium's inherent qualities as a natural polymer provide impressive insulation, fire resistance, and acoustic and thermal energy absorption properties, making it adaptable to diverse project requirements through Ecovative's research and development modifications.
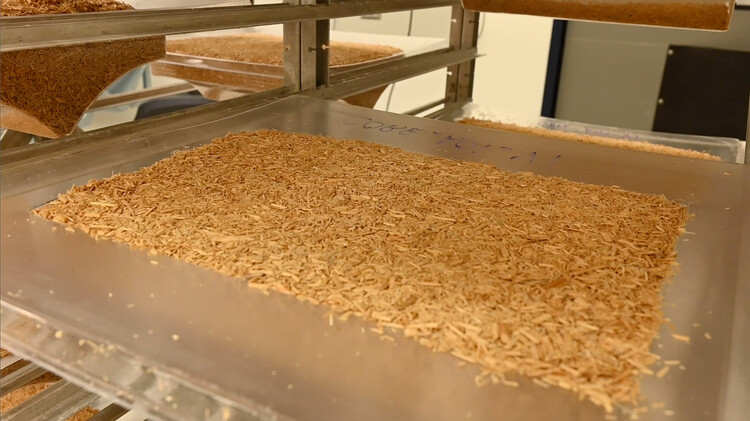

The growing process takes only days and requires minimal energy, as most of the process takes place at ambient room temperature. The material's service life when sandwiched between the Fiber Reinforced Panels is impressively indefinite, and if at any time a section is damaged or needs to be replaced, the MycoComposite mycelium material can be easily regrown and replaced, highlighting its sustainability and long-term viability. —Thomas VanHaren
The façade is composed of shredded hemp, which captures carbon twice as effectively as forests and is naturally bonded through the mycelium's intricate network of roots. This creates a powerful tool for retaining carbon, reducing the project's carbon footprint. The natural properties of the mycelium polymer provide insulation similar to fiberglass and rock wool (R-value of 3 per inch), fire resistance, and acoustic/thermal energy absorption, ideal for noise reduction in urban environments. In addition, Ecovative's research team adapted the growth processes to meet the specific needs of the project, highlighting the material's adaptability and performance potential.
Fast, Prefabricated Construction
The innovative approach is not just limited to design or innovative materials; it extends to the construction phase too. Factory_OS, the construction partner, employs industrialized construction methods, treating buildings more as products than as one-offs. This approach reduces waste, time, and costs while ensuring greater safety and reliability. By prefabricating housing modules in a factory and assembling them on-site, the team achieved an unprecedented completion time of around two weeks, a fraction of the time that traditional construction processes would require.
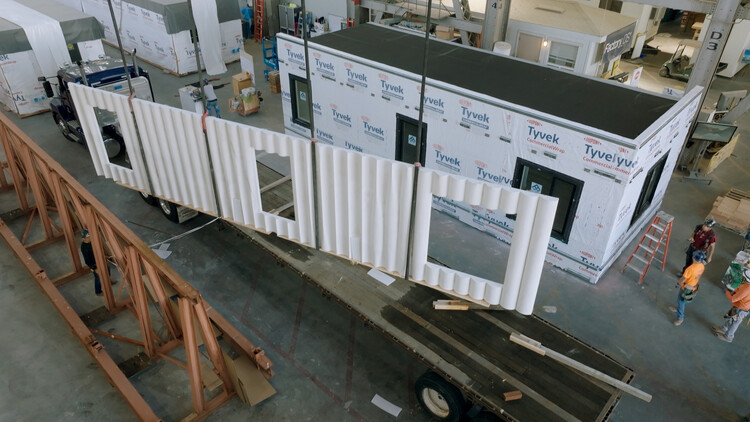
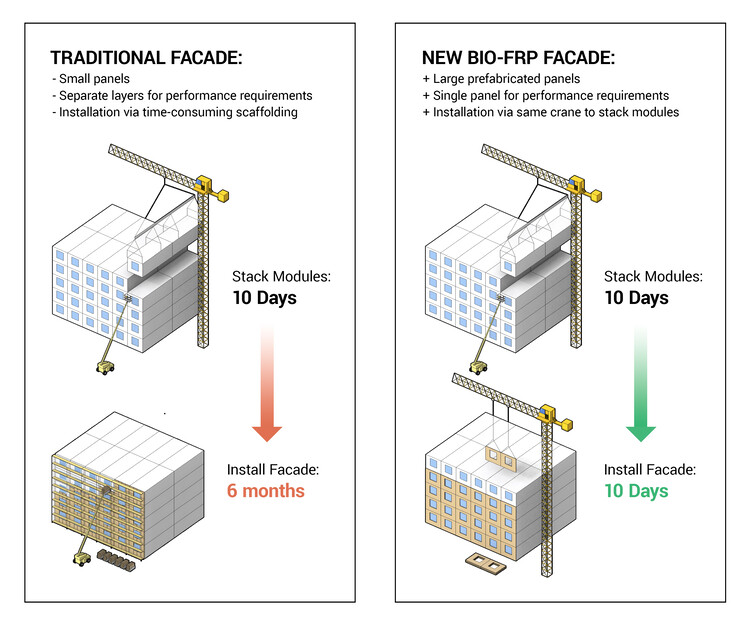

This innovative approach not only drastically reduced construction time but also incorporated carbon sequestration properties, setting new standards for sustainability in building materials. The California Housing Accelerator has driven the development of Phoenix, offering substantial incentives for affordable housing initiatives that overcome the limitations of traditional design and construction methods while achieving ambitious deadlines. Successfully meeting this challenge is the key to accessing billions of dollars in subsidies for new housing construction in this North American state, and navigating this opportunity requires innovative and creative solutions at every stage of the process.
Projects like this promise to provide high-quality, low-carbon housing to communities, while influencing global transformation in the built environment. This pioneering effort signifies a fundamental shift towards sustainable, efficient, and scalable housing solutions. As this exemplary project is completed, its innovations will be poised to scale up, shaping the future of affordable housing and sustainable construction around the world. Phoenix is more than just a housing project; it is a testament to the power of innovative technology and interdisciplinary collaboration. By harnessing computational resources, the project changes the standard for typical multi-family projects in the San Francisco Bay Area, ushering in a future where affordability, sustainability, and speed of construction converge harmoniously for the betterment of society and the planet.


















